CD56 Antibody

CD56 Antibody
| Name |
Anti-Human CD56 antibody |
| Description |
Mouse monoclonal antibody, cultured in vitro |
| Catalog # |
K106m1 |
| Specification |
1xPBS,pH7.4 |
| Purity |
Purity>98%, purified by Protein A/G chromatography |
| Storage |
Aliquot and store at -80°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Label |
P-phycoerythrin (PE) |

Product Information
Flow-cytometry platform
Whole blood samples were stained with CD56-PE antibody, and the expression of CD56 cells was analyzed by BD FACSCanto™ II flow cytometer. CD56 lymphocytes grouping were clearly observed.
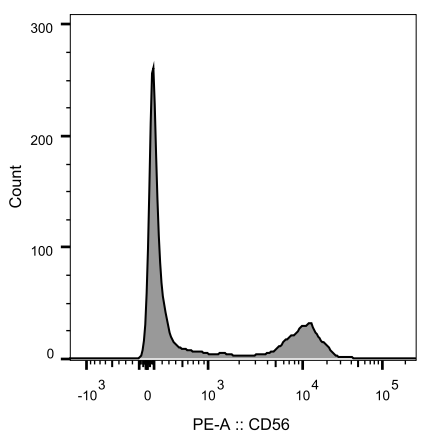
Fig.1 Flow cytometry analysis of CD56 expression in lymphocytes of human peripheral blood

Introduction to CD56 Molecule
CD56 is an isoform of neural cell adhesion molecule and is a specifically differentiated antigen of NK cells. It plays an important role in the diagnosis of small cell carcinoma (such as small cell esophageal cancer and small cell lung cancer) and lymphoid hematopoietic system diseases.
Clinically, the expression intensity of CD56 molecule and CD16 molecule is often detected jointly to distinguish NK cells. According to the characteristics that NK cells do not express CD3 molecules, the flow cytometry platform circled the CD3-negative lymphocyte population, and then divided NK cells into three cell subpopulations: CD56+, CD56+CD16+ and CD16+ according to whether CD56 and CD16 molecules were expressed. NK cells in the human body are mainly CD3-CD56+ lymphocytes, accounting for about 70%, which can be expressed in a variety of tumors, and can exhibit natural killing activity without binding to antigens. What’s more, it can also indicate the anti-tumor ability of NK cells in malignant tumors. CD56+ NK cell subsets kill target cells mainly through two pathways: one is the expression of Fas ligand (FasL), which can bind to the corresponding receptor on the surface of target cells to induce apoptosis of target cells. The other is releasling granzyme B and perforin to destroy the membranes and mitochondria of target cells, and then cytochrome C is released to induce apoptosis. CD56 is also present on the surface of partial T cells. In recent years, it has been found that NK/T cells (CD3+CD56+) can exert cytotoxic effects to kill tumor cells by promoting the proliferation and activation of T cells, especially in hematological tumors such as leukemia and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. At the same time, CD56+ T cells have the function of resisting AIDS infection, and exhibit inhibitory activity on both clinically isolated strains and laboratory cultured strains of HIV.
References
[1] Hou W ,LiY , Ho W . CD56+ T cells inhibit HIV-1 infection of macrophages[J].J Leukoc Biol, 2012, 92(2):343-351.

Related Products

