| Name | Anti-Human Heparin-binding protein (HBP) antibody | ||||||
| Catalog # | R439n4 | R440e8 | R441c3 | R442e3 | R152c7 | R153a2 | R236e3 |
| Platforms Pairs |
Chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) | Immunochromatography assay (ICA) | |||||
| R439n4 (Capture) -R440e8 (Detection) R440e8 (Capture) -R153a2 (Detection) R152c7 (Capture) -R153a2 (Detection) |
R442e3 (Capture) -R441c3 (Detection) R152c7 (Capture) -R236e3 (Detection) |
||||||
| Description | Rabbit monoclonal antibody, cultured in vitro | monoclonal antibody, cultured in vitro | |||||
| Buffer | 1xPBS,pH 7.4 | ||||||
| Purity | Purity>95%, purified by Protein A/G chromatography | ||||||
| Storage | Aliquot and store at -20°C or lower. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. | ||||||
| Name | Heparin-binding protein (HBP) antigen | |||
| Description | Recombinant, C-terminal His-tagged, in vitro expressed from mammalian cells | |||
| Applications | Calibrator and quality control product | |||
| Catalog # | K1523 | |||
| Uniprot ID | P20160 | |||
| Purity | >>90%, analyzed by R250-stained SDS-PAGE | |||
| Buffer | 1xPBS,pH 7.4 | |||
| Storage | Aliquot and store at -80°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. | |||
| SDS-PAGE |
Predicted MW around 25kDa (tagged)
|
|||
HBP Antigen K1523 was used to detect the rabbit HBP monoclonal antibody R439n4, R440e8, R441c3, R442e3 on ELISA platform, whose EC50 was 2.47ng/mL, 1.41ng/mL, 3.28ng/mL, 2.69ng/mL, respectively.
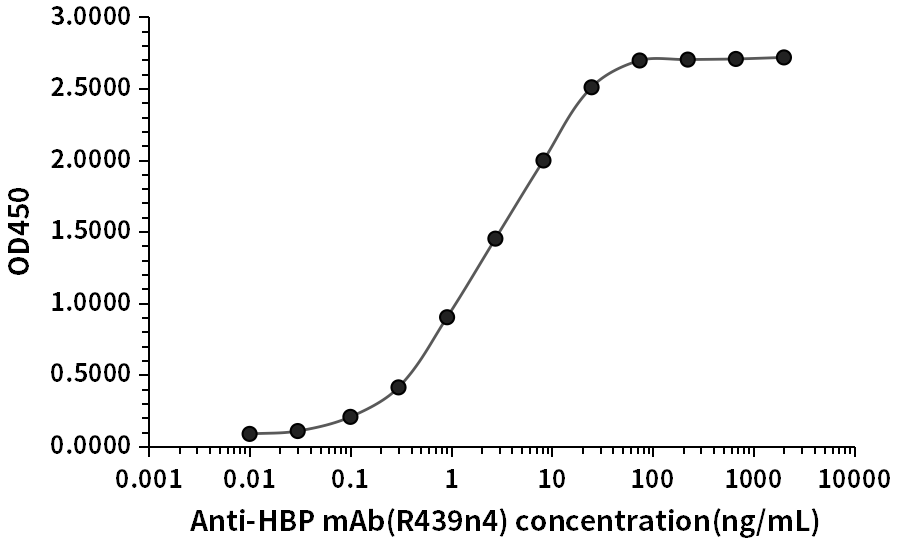
Fig.1 HBP antibody (R439n4) ELISA result
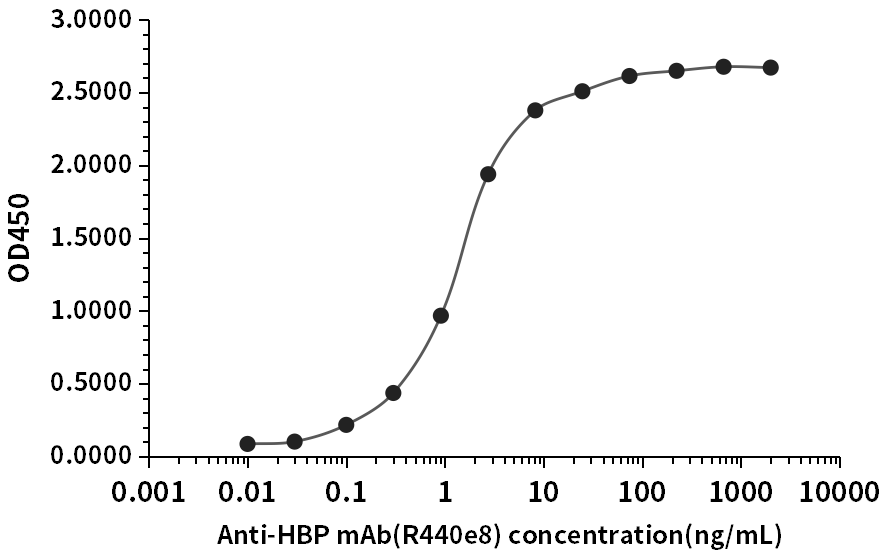
Fig.2 HBP antibody (R440e8) ELISA result
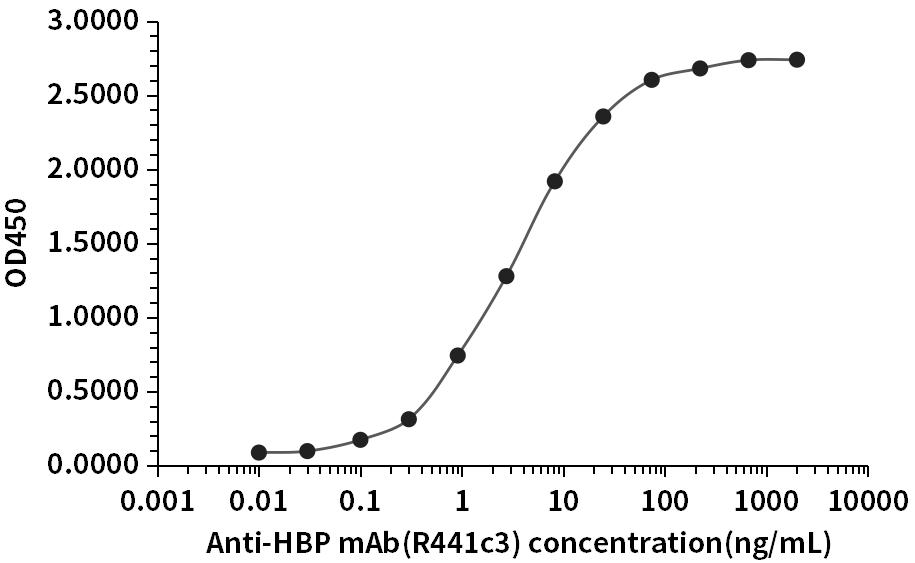
Fig.3 HBP antibody (R441c3) ELISA result
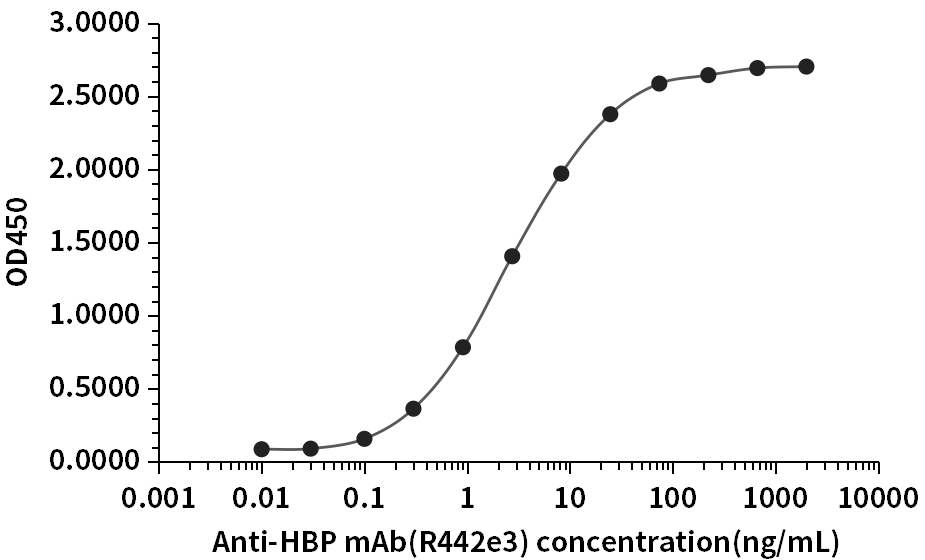
Fig.4 HBP antibody (R442e3) ELISA result
Correlation in clinical samples
R440e8-R153a2 matched antibody pair was verified in JOINSTARTM serum assigned samples (51 cases, concentration: 3.05-298.55ng/mL, clinical coefficient of determination R2 > 0.98).
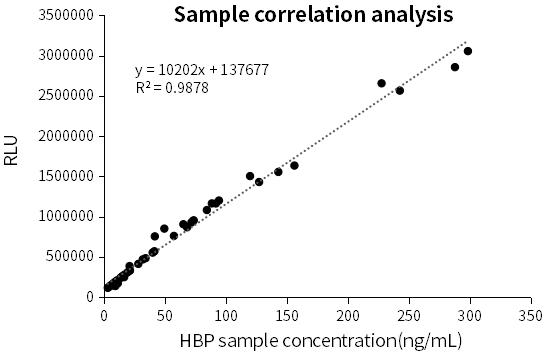
Fig.5 Correlation of HBP on CLIA platform in clinical samples
| Sample No. | Concentration (ng/mL) |
RLU |
| 1 | 3.05 | 118238 |
| 2 | 4.16 | 131421 |
| 3 | 5.32 | 145199 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 50 | 287.91 | 2856594 |
| 51 | 298.55 | 3055494 |
Table.1 Correlation data in clinical samples
R439n4-R440e8 matched antibody pair was verified in JOINSTARTM serum assigned samples (51 cases, concentration: 3.05-298.55ng/mL, clinical coefficient of determination R2 > 0.98).
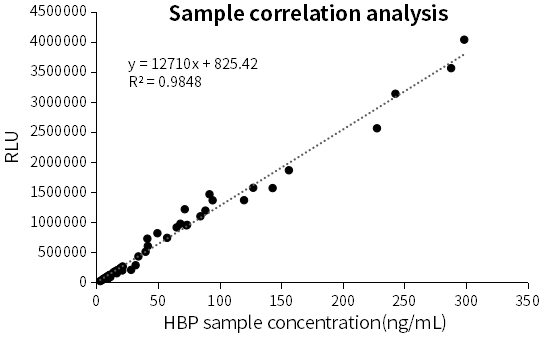
Fig.6 Correlation of HBP on CLIA platform in clinical samples
| Sample No. | Concentration (ng/mL) |
RLU |
| 1 | 3.05 | 20110 |
| 2 | 4.16 | 34839 |
| 3 | 5.32 | 50231 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 50 | 287.91 | 3565694 |
| 51 | 298.55 | 4039815 |
Table.2 Correlation data in clinical samples
Correlation in clinical samples
R440e8-R153a2 matched antibody pair was verified in JOINSTARTM serum assigned samples (21 cases, concentration: 0-298.55ng/mL, clinical coefficient of determination R2 > 0.95).
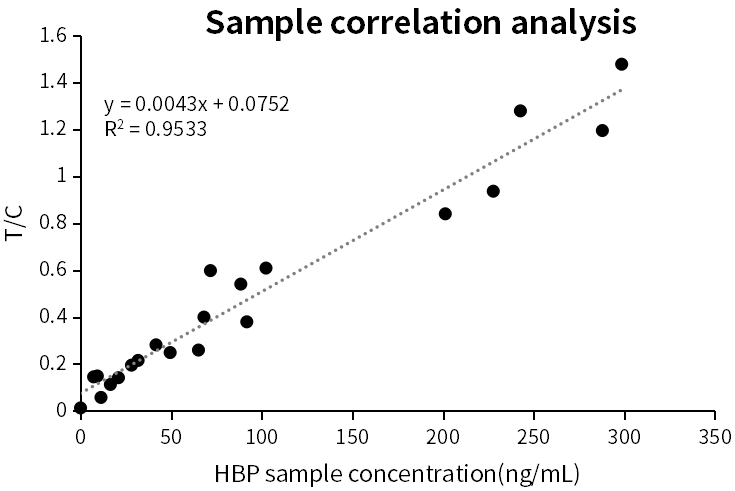
Fig.7 Correlation of HBP on CLIA platform in clinical samples
| Sample No. | Concentration (ng/mL) |
T/C |
| 1 | 0 | 0.0128 |
| 2 | 7.22 | 0.1453 |
| 3 | 9.28 | 0.1489 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 50 | 287.91 | 1.1946 |
| 51 | 298.55 | 1.4773 |
Table.3 Correlation data in clinical samples
References
[1] Linder A, Akesson p, Inghammar M, et al. Elevated plasma levels of heparin-binding protein in intensive care unit patients with severe sepsis and septic shock [J]. Crit Care, 2012, 16(3): R90.
[2] Dankiewicz J , Linder A, Annborn M, et al. Heparin-binding protein: an early indicator of critical illness and predictor of outcome in cardiac arrest [J]. Resuscitation, 2013, 84(7): 935-939.
