Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 (PD-1)
Human Recombinant PD-1 Protein
| Name |
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) |
| Alternative Names |
CD279 protein, hPD-1 protein, hSLE1 protein, SLEB2 protein, PDCD1 protein |
| Catalog # |
P1210 |
| Uniprot ID |
Q15116.3 |
| Description |
C-terminal His-tagged PD-1 fusion protein, derived from mammalian expression system, expressed by transfected HEK293 cells |
| Purity |
> 90%, analyzed by SDS-PAGE |
| Species |
Human |
| MW |
Around 17.5kDa |
| Endotoxin Level |
< 1EU/μg, analyzed by LAL assay<1EU/μg |
| Storage |
Lyophilized powder 4°C valid for 3 years, -20°C after rehydration valid for 1 year. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| SDS-PAGE |
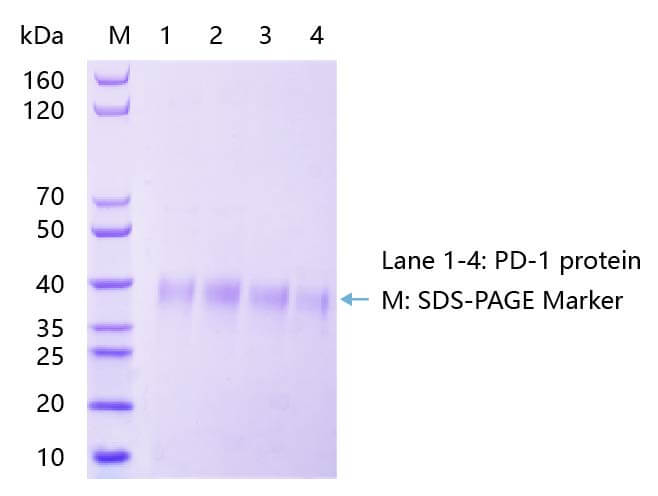 |
Introduction to programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), also known as PDCD1, is an important immunosuppressive membrane protein expressed on the surface of T cells. The PD-1 of human adults consists of an extracellular domain (ECD) with 148 amino acids, an immunoglobulin V-set domain with 24 transmembrane amino acids and cytoplasmic domain with 95 amino acids. The ECD of human PD-1 shares 65% sequence identity with the ECD of mouse PD-1.
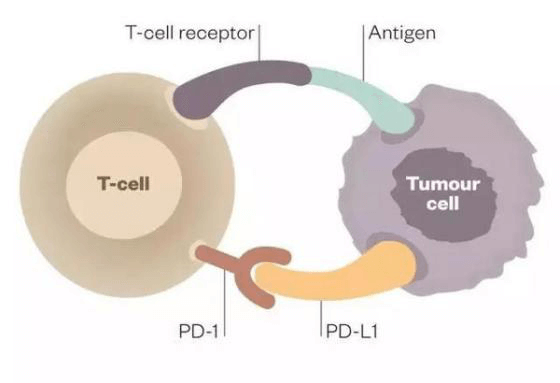
PD-1 has two ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2. In the tumor microenvironment, tumor cells can express PD-L1 or PD-L2. One way for tumor cells to escape from immune system is connecting the these ligands to the PD-1 proteins of T cells.
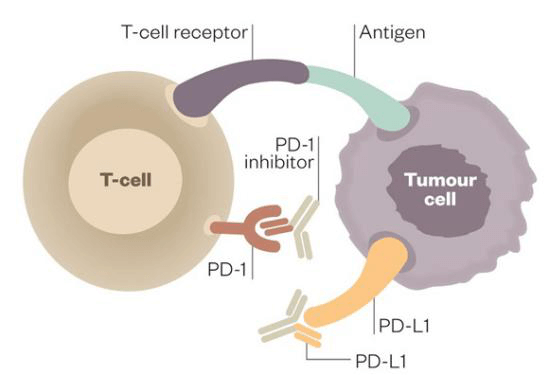
When the ligands is connected to PD-1, the activation, proliferation, and secretion of T cell cytokines (including IL-1, IL-4, IL-10, and IFN-γ) are then inhibited, thus makes T cells unable to recognize and send signals to the immune system to attack the tumor cells, ultimately suppressing the immune response. By blocking the connection between PD-1 and its ligand through antibody or genetic manipulation, the eradication of tumors can be accelerated and the immunotherapy for cancers can be improved.
References
[1] Butte, Manish J. , et al. Programmed death-1 ligand 1 interacts specifically with the B7-1 costimulatory molecule to inhibit T cell responses. Immunity 2007, 27(1):111-122.
[2] Iwai, et al. Involvement of PD-L1 on tumor cells in the escape from host immune system and tumor immunotherapy by PD-L1 blockade. PNAS, 2002,99 (19):12293-12297.
[3] Kalim, Muhammad , et al. Construction of High Level Prokaryotic Expression and Purification System of PD-L1 Extracellular Domain by using Escherichia coli Host Cell Machinery. Immunology Letters, 2017, 190:34-41.

Related Products